ここで学習すること
ランダムフォレストの特徴と実際のプログラム事例を学習します。
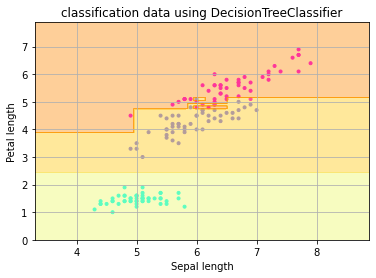
ランダムフォレストは多数の決定木を作り、分類の結果を多数決できめる方法です。
ランダムフォレストの決定木はランダムに決められた一部の説明変数を使用して分類を行います。このようにして得られた分類のうちもっとも多い分類パターンを結果とします。
決定木とはことなり線形分離以外の分類も可能です。
ランダムフォレストはscikit-learnのensembleモジュール内のRandomForestClassifier()で実行できます。
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
irisデータを読み込みます。詳細は機械学習9|決定木を参照ください。
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [0, 2]]
y = iris.target
train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size0.2, random_state =42)
ランダムフォレストのモデル作成します
model = RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
可視化プログラムです。詳細は機械学習9|決定木を参照ください。
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, marker=”.”, cmap=matplotlib.cm.get_cmap(name=”cool”), alpha=1.0)
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() – 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() – 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, 0.02), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, 0.02))
Z = model.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T).reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.3, cmap=mtplotlib.cm.get_cmap(name=’Wistia’))
plt.xlabel(‘sepal’)
plt.ylabel(‘petal’)
plt.grin(True)
plt.show